Your organs perform the most vital functions of keeping your body alive. They pump blood, filter it, regulate hormones, and more. An organ doesn’t have to be large to be important, but it’s always interesting to know what the largest organs are.
Medically speaking, an organ is a cluster of tissue with a specific purpose. This structure is opposed to muscle, bone, tendon, or some other composition of cells that may or may not do only one thing.
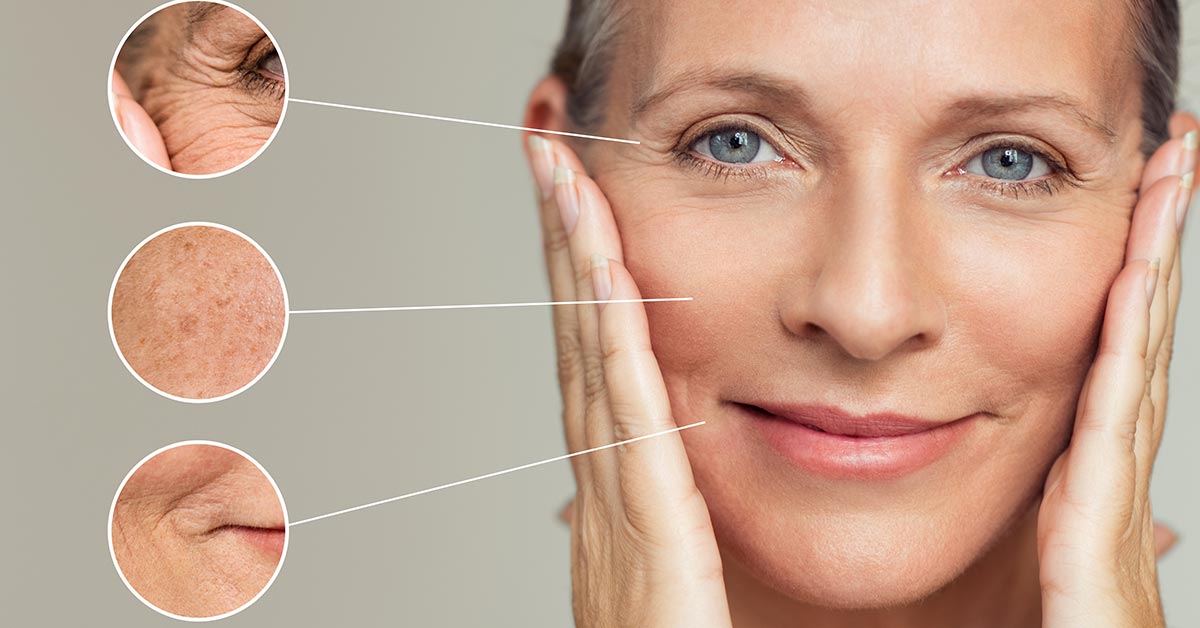
According to many experts, there are 79 organs in the human body. But some estimate that there are more. The skin is currently the largest known organ. But there is a contender that may prove to be the largest with more research. It is called the interstitium.
The Largest Organ Is the Skin
More research is needed on the interstitium, so for now the largest organ is the skin.
This amazing organ covers the entire body. It comprises about 16 percent of the body mass.
The skin has several purposes.
- It regulates your body temperature.
- It protects your body from the environment and germs.
- It stores water, vitamin D, and fat.
- It processes sensory input.
Skin Facts
There are over 3,000 skin disorders.
The skin has three layers: the dermis, the epidermis, and the hypodermis. These stacked layers hold water, sweat glands, body fat, nerves, oil glands, hair follicles, and more.
The skin’s functions are many, and they include protecting us from damaging UV rays.
The skin has interesting interactions with other organs. You can see from the facts below that skin function can be impacted by many other organs, but it also impacts the other organs because it regulates so much fluid and processes sunlight.
Where Does Skin Color Come From?
Skin color is created with melanin. People with darker skin have both more and deeper-colored melanin particles than fairer people.
Original humans had darker skin, whereas fair skin is an adaptation to mostly northern climates. Fairer skin allows people to absorb more UV, helping them to process more vitamin D.
The interstitium
The interstitium hasn’t been studied much compared to other organs. The body of research that put it on the map as a possible organ was completed in 2018.
This mass holds nearly 93 percent of your body fluid. It is a series of spaces in the body filled with fluid. The spaces are made of flexible connective tissue, but you’d be right in assuming that everyone may not agree that this constitutes an organ.
Being mostly space, the interstitium is nevertheless very important tissue. Much of it resides under the skin, but some of it is attached to the body’s connective tissue. It is also found around the arteries and veins and in the linings of your lungs, digestive tract, and urinary system.
The Liver
The liver is the largest solid organ inside the body. It is approximately the size of a football and weighs between three and three-and-a-half pounds.
The liver has several important functions.
- It produces bile.
- It detoxifies the blood.
- It makes blood proteins.
- It turns sugars into glycogen.
- It helps clot the blood properly.
The liver holds about a pint of blood at a time.
The Brain
The brain is the second largest internal organ after the liver in almost all humans.
The brain weighs about three pounds also.
It is generally about 5.5 inches by 6.5 inches by 3.6 inches.
The brain does very important things for the body, including regulating thoughts and feelings. It processes information, controls behavior, and interprets the physical sensations people have.